关于2018年国民经济和社会发展计划执行情况与2019年国民经济和社会发展计划草案的报告文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
Report on the Implementation of the 2018 Plan for National Economic and Social Development and on the 2019 Draft Plan for National Economic and Social Development文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
——2019年3月5日在第十三届全国人民代表大会第二次会议上文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
Delivered at the Second Session of the Thirteenth National People’s Congress on March 5, 2019文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
国家发展和改革委员会文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
National Development and Reform Commission文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
各位代表:文章源自英文巴士-https://www.en84.com/6797.html
Esteemed Deputies,
受国务院委托,现将2018年国民经济和社会发展计划执行情况与2019年国民经济和社会发展计划草案提请十三届全国人大二次会议审议,并请全国政协各位委员提出意见。
The National Development and Reform Commission has been entrusted by the State Council to deliver this report on the implementation of the 2018 plan and on the 2019 draft plan for national economic and social development to the Second Session of the 13th National People’s Congress (NPC) for your deliberation. It also invites comments from the members of the National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC).
一、2018年国民经济和社会发展计划执行情况
I. Implementation of the 2018 Plan for National Economic and Social Development
2018年,面对错综复杂的国际环境和艰巨繁重的国内改革发展稳定任务,在以习近平同志为核心的党中央坚强领导下,各地区各部门以习近平新时代中国特色社会主义思想为指导,深入贯彻党的十九大和十九届二中、三中全会精神,增强“四个意识”,坚定“四个自信”,做到“两个维护”,按照党中央、国务院决策部署,统筹推进“五位一体”总体布局,协调推进“四个全面”战略布局,坚持稳中求进工作总基调,贯彻新发展理念,落实高质量发展要求,以供给侧结构性改革为主线,认真执行十三届全国人大一次会议审议批准的《政府工作报告》、2018年国民经济和社会发展计划,落实全国人大财政经济委员会的审查意见、十三届全国人大常委会第七次会议对“十三五”规划《纲要》实施中期评估报告的审议意见等,大力推进市场化改革、高水平开放,大力推进现代化经济体系建设,坚决打好防范化解重大风险、精准脱贫、污染防治三大攻坚战,有效应对外部环境深刻变化,统筹稳增长、促改革、调结构、惠民生、防风险,着力做好稳就业、稳金融、稳外贸、稳外资、稳投资、稳预期工作,经济保持总体平稳、稳中有进,全年经济社会发展主要目标任务较好完成,计划执行情况总体良好。
In 2018, we were confronted with a complex and volatile environment internationally and formidable tasks in promoting reform, development, and stability at home. Under the strong leadership of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC) with Comrade Xi Jinping at its core and the guidance of Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, all regions and departments fully implemented the guiding principles of the 19th CPC National Congress and the second and third plenary sessions of the 19th CPC Central Committee. We strengthened our consciousness of the need to maintain political integrity, think in big-picture terms, follow the leadership core, and keep in alignment; increased our confidence in the path, theory, system, and culture of socialism with Chinese characteristics; and resolutely upheld General Secretary Xi Jinping’s core position on the Party Central Committee and in the Party as a whole, and resolutely upheld the Party Central Committee’s authority and its centralized, unified leadership.
In accordance with the decisions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council, we pursued coordinated implementation of the five-sphere integrated plan and the four-pronged comprehensive strategy. We stayed committed to the underlying principle of pursuing progress while ensuring stability, followed the new development philosophy, fulfilled the requirement for high-quality development, and took supply-side structural reform as our main task. We implemented the Report on the Work of the Government and the 2018 Plan for National Economic and Social Development approved at the First Session of the 13th NPC, and adopted the suggestions from the review of the 2018 Plan by the NPC Financial and Economic Affairs Committee, as well as those put forth at the 13th NPC Standing Committee’s Seventh Session regarding the midterm assessment report on the implementation of the 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020).
We focused on promoting market-oriented reforms and high-standard opening-up, worked hard to develop a modernized economy, and delivered solid progress in the critical battles against potential risk, poverty, and pollution. We responded effectively to major changes in the external environment, and took coordinated steps to achieve steady growth, advance reform, make structural adjustments, improve living standards, and guard against risk. We worked to ensure stability in employment, financial operations, foreign trade, foreign investment, domestic investment, and expectations. The economy maintained general stability and registered good progress, the main targets and tasks in economic and social development for the year were accomplished, and implementation of the 2018 Plan was successful overall.
(一)着力创新和完善宏观调控,经济运行保持在合理区间。更好发挥国家发展规划的战略导向作用,保持宏观经济政策的连续性和稳定性,坚决不搞“大水漫灌”式强刺激,在区间调控的基础上加强定向调控、精准调控、相机调控,主动预调微调、强化政策协同、做好预期管理,稳妥应对中美经贸摩擦,保持了经济平稳健康发展。
1. We employed new and improved methods of macro regulation and ensured major economic indicators stayed within an appropriate range.
We gave better play to the guiding role of national development plans to ensure continuity and stability between macroeconomic policies. We refrained from resorting to a deluge of strong stimulus policies. Instead, we strengthened targeted, precision, and well-timed regulation on the basis of range-based regulation. We took proactive measures to carry out anticipatory adjustments and fine-tuning, strengthened coordination between macroeconomic policies, and better managed expectations. We appropriately handled economic and trade friction between China and the US. With these efforts, we were able to maintain stable and sound economic development.
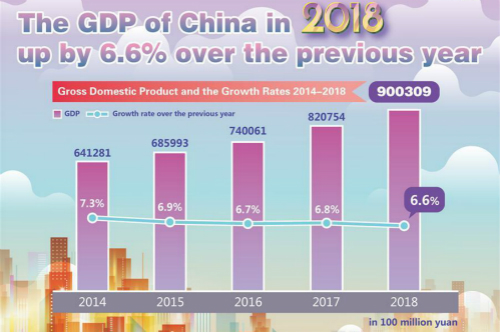
一是宏观调控目标较好完成。国内生产总值达到90.03万亿元,增长6.6%,符合预期目标。实施更加积极的就业政策,建立完善稳就业应急机制,创新创业带动就业的作用进一步增强,全年城镇新增就业1361万人,全国城镇调查失业率稳定在5%左右的较低水平。加强价格监测分析预警调控,做好市场保供稳价工作,全年居民消费价格温和上涨2.1%。国际收支基本平衡,外汇储备稳定在3万亿美元以上。
1) Macro-regulation targets were achieved.
China’s gross domestic product (GDP) reached 90.03 trillion yuan, an increase of 6.6%, which was in line with the projected target. We implemented a more proactive employment policy, and established a sound emergency response mechanism to keep employment stable. More jobs were created through innovation and business startups. A total of 13.61 million urban jobs were added over the year, and the survey-based urban unemployment rate was kept at a relatively low level of about 5%. For prices we strengthened monitoring, analysis, early warning, and regulation, and ensured market supply and price levels remained stable. The consumer price index (CPI) registered a moderate rise of 2.1% for the year. A basic equilibrium was kept in the balance of payments and foreign exchange reserves were stable at over US$ 3 trillion.
二是财政金融运行基本平稳。积极的财政政策聚力增效,减税降费力度进一步加大,财政支出结构持续优化,有力保障民生等重点领域资金需求。全国一般公共预算收入18.34万亿元,增长6.2%;全国一般公共预算支出22.09万亿元,增长8.7%;财政赤字2.38万亿元,与预算持平。稳健的货币政策保持中性,通过差别化准备金、差异化信贷等政策,引导资金更多投向民营企业和小微企业等实体经济。国家融资担保基金设立运作。年末广义货币(M2)余额增长8.1%。
2) Fiscal and financial indicators were stable.
We implemented a proactive fiscal policy with greater intensity and enhanced its performance. Further steps were taken to cut taxes and fees, and efforts to improve the composition of government spending continued, to ensure funding for major areas such as the improvement of living standards. Revenue in the general public budget was 18.34 trillion yuan, an increase of 6.2%; expenditure totaled 22.09 trillion yuan, an increase of 8.7%; and the fiscal deficit was 2.38 trillion yuan, the same as the budgeted figure. In monetary policy, a prudent and neutral stance was maintained, and we used policies of differentiated reserve ratios and differentiated credit to guide more funding toward private enterprises and small and micro businesses in the real economy. The national financing guaranty fund was put into operation. At the end of 2018, growth in the balance of the M2 money supply was 8.1%.
三是投资补短板力度持续加大。充分发挥中央预算内投资对优化供给结构的引导带动作用,建立加大基础设施领域补短板力度协调机制,加强重大项目储备,统筹推进重大基础设施规划建设,铁路营业里程超过13.1万公里,其中高速铁路超过2.9万公里;高速公路总里程达到14.3万公里。促进民间投资持续健康发展,在铁路、民航、油气、电信等领域向民间资本推出一批有吸引力的项目,规范有序推广政府和社会资本合作(PPP)模式。固定资产投资(不含农户)增长5.9%,其中民间投资增长8.7%。投资结构持续优化,高技术制造业、装备制造业投资分别增长16.1%和11.1%。
3) Investment in areas of weakness continued to increase.
We enabled investment from the central government budget to play a leading role in improving the supply structure. We established a mechanism to strengthen coordination in shoring up infrastructure weaknesses, added to the major project reserve, and coordinated the planning and construction of major infrastructure projects. The length of in-service railways exceeded 131,000 kilometers, including more than 29,000 kilometers of high-speed rail lines. The total length of expressways now stands at 143,000 kilometers. To encourage sustainable and healthy private investment, we rolled out a number of attractive projects in sectors like rail, civil aviation, oil and natural gas, and telecommunications, and the public-private partnership (PPP) model was extended to more areas in a well-regulated and orderly way. Total fixed-asset investment (excluding rural households) increased by 5.9%, which includes an 8.7% increase in private investment. There were continuous improvements in the composition of investment, with investment in high-tech manufacturing and equipment manufacturing growing 16.1% and 11.1% respectively.
四是消费提质扩容积极推进。完善促进消费体制机制进一步激发居民消费潜力的若干意见和三年实施方案出台实施,放心消费创新活动深入推进,消费环境持续优化。降低药品、汽车、日用消费品等进口关税,调整完善新能源汽车推广应用财政补贴政策。加快提升新型信息产品供给体系质量,信息消费保持快速增长。海南省建设国际旅游消费中心的实施方案、促进乡村旅游发展提质升级行动方案(2018年-2020年)印发实施,引导城乡居民扩大文化消费试点工作持续推进,上千家重点国有景区门票价格下降,全国家政培训提升行动启动,相关领域消费潜力进一步释放,全年社会消费品零售总额增长9%。消费对经济增长拉动作用增强,最终消费支出贡献率提高到76.2%。
4) Strong improvements in the quality and scale of consumption were achieved.
The Guidelines on Improving Consumption-Promoting Systems and Mechanisms to Unleash the Potential of Personal Consumption were implemented, along with a three-year action plan. The campaign to create a worry-free atmosphere for consumers yielded further progress and helped improve the consumption environment. We lowered import tariffs on medicines, automobiles, and some non-durable consumer goods, and improved government subsidy policies for promoting the use of new-energy vehicles (NEVs). We improved the supply system for new types of information products at a faster pace and maintained rapid growth in information consumption. We unveiled and put in motion the Implementation Plan on Making Hainan an International Hotspot for Tourism and Shopping and the Action Plan on Improving and Upgrading Rural Tourism (2018-2020). Trials to boost cultural consumption among urban and rural residents continued, over 1,000 key state tourist sites cut their ticket prices, and a national training program was launched in the domestic services sector, thus further unleashing the potential for consumption in relevant areas. Total annual retail sales of consumer goods rose 9%. With a contribution of 76.2% of growth, consumption is playing a much bigger role in driving the economy.
(二)供给侧结构性改革深入推进,高质量发展取得积极进展。着力进行推动高质量发展的顶层设计,制定实施推动高质量发展的意见,推动高质量发展的制度体系逐步建立。扎实推进供给侧结构性改革,以“破、立、降”为主攻方向,持续改善供给结构,发展质量效益稳步提升。
2. We steadily advanced supply-side structural reform and made strong progress toward high-quality development.
We focused on top-level planning to promote high-quality development. We implemented the Guidelines on Promoting High-Quality Development, and took gradual steps toward establishing an institutional system for high-quality development. We continued to make solid progress in supply-side structural reform. With the focus on cutting ineffective supply, fostering new growth drivers, and reducing costs in the real economy, we saw yet further improvements in the composition of supply and sustained increases in the quality and efficiency of development.
一是去产能工作扎实开展。结构性去产能、系统性优产能持续推进,压减粗钢产能3500万吨以上、退出煤炭落后产能2.7亿吨,均提前两年完成“十三五”目标任务,一大批“散乱污”企业出清,工业产能利用率处在较高水平。进一步做好“僵尸企业”及去产能企业债务处置工作,稳妥推进去产能职工安置,转岗再就业工作平稳有序进行。
1) Solid progress was achieved in cutting overcapacity.
Our efforts to cut overcapacity through structural adjustments and improvements continued. We cut production capacity by over 35 million metric tons of crude steel and 270 million metric tons of coal, thus achieving the targets for steel and coal overcapacity cuts in the 13th Five-Year Plan two years ahead of schedule. A large number of small, poorly-managed, and heavily-polluting enterprises were closed down, and a relatively high rate of industrial capacity utilization was maintained. Further progress was made in handling the debts of “zombie enterprises” and enterprises with excess capacity, and proper steps were taken to help workers displaced due to overcapacity cuts, ensuring they were resettled to new positions or found new employment in a smooth and orderly fashion.
二是振兴实体经济迈出新步伐。制造强国建设持续推进,工业增加值突破30万亿元。促进首台(套)重大技术装备示范应用的意见印发实施,关键核心技术攻关加快开展。增强制造业核心竞争力三年行动计划(2018-2020年)、工业互联网发展行动计划(2018-2020年)深入实施,推动互联网、大数据、人工智能和实体经济深度融合,推进工业互联网+智能制造集成应用示范,轨道交通、高端医疗器械、工业机器人等制造业重点领域关键技术加快突破并实现产业化。新一轮技术改造升级工程组织实施,高端装备、智能制造、新材料等重点领域技术改造加快推进。质量强国战略深入实施,标准质量品牌建设持续加强。国家物流枢纽布局和建设规划印发实施。服务业创新发展大纲深入落实,服务质量提升专项行动加快推进,服务业综合改革试点深入开展。
2) New strides were taken in revitalizing the real economy.
As progress continued in building China into a manufacturer of quality, the total value-added of industry broke the 30-trillion-yuan mark. We promulgated the Guidelines on Promoting the Demonstration and Application of Newly-Developed Major Technological Equipment, and stepped up efforts to make breakthroughs in a number of core and key technologies. We moved forward with the implementation of the Three-Year Action Plan on Enhancing Core Competitiveness in the Manufacturing Sector (2018-2020) and the Action Plan on Developing the Industrial Internet (2018-2020). We promoted the in-depth integration of the internet, big data, and artificial intelligence (AI) into the real economy, and carried out demonstration projects for integrated applications of the industrial internet plus smart manufacturing. Breakthroughs were made at a faster pace in core technologies in key areas such as rail transit, high-end medical appliances, and industrial robots, and these have been successfully applied to industry. We carried out a new round of technology transformation and upgrading projects, and accelerated technology transformations in major areas such as high-end equipment, smart manufacturing, and new materials. Further strides were taken in the strategy to make China a country strong on quality, and our work on strengthening quality, standards, and brands was intensified. We issued the Plan on the Layout and Development of National Logistics Hubs. In the services sector, we continued implementing the guidelines on innovation-driven development, carried out dedicated campaigns to raise quality, and conducted trials of integrated reform.
三是降成本工作持续推进。大力实施减税降费,全年为企业和个人减负约1.3万亿元。制造业等行业增值税税率从17%降至16%,交通运输、邮政、建筑、基础电信服务等行业及农产品等货物的增值税税率从11%降至10%,提高小规模纳税人年销售额标准,研发费用加计扣除比例提高到75%的政策扩大至所有企业,金融机构免征增值税贷款单户授信额度提高到1000万元。降低、停征一批行政事业性收费和政府性基金。延长阶段性降低社会保险费率和企业住房公积金缴存比例政策期限,清理规范经营服务性收费。大力推动降低用能、物流等成本,市场化交易电量比重进一步提高,全国一般工商业电价平均降低10%的目标超额完成,对挂车减半征收车辆购置税,扩大高速公路差异化收费试点。
3) Work on bringing down costs continued.
We stepped up efforts to reduce taxes and fees, helping ease the burden on enterprises and individuals by about 1.3 trillion yuan for the year. The rates of value added tax (VAT) were lowered from 17% to 16% in manufacturing and some other industries, and from 11% to 10% in industries such as transportation, postal services, construction, and basic telecommunications services and on goods such as agricultural products. The annual sales threshold for small-scale taxpayers was raised. The policy of a 75% tax deduction for research and development (R&D) expenses was extended to cover all enterprises. Financial institutions’ credit line threshold for VAT exemption rose to 10 million yuan. We reduced or abolished a range of government administrative fees and government-managed funds. We continued the policy of reducing businesses’ contributions to social insurance schemes and the housing provident fund, and overhauled and standardized business service fees. We took strong steps to lower energy and logistics costs, and continued to raise the proportion of market-based electricity transactions. The target to cut the price of electricity for general industrial and commercial businesses by an average of 10% was surpassed. Purchase tax on trailers was halved, and the policy of differentiated tolls was extended to cover more expressways.
(三)扎实打好三大攻坚战,重点任务取得积极进展。制定三大攻坚战行动方案,依法依规有序实施,金融治理效果明显,脱贫攻坚完成年度目标,生态环境状况明显好转。
3. We made solid progress in the critical battles against potential risk, poverty, and pollution, and yielded positive results in key tasks.
We formulated an action plan for winning the three critical battles, for which implementation has proceeded as planned and in accordance with laws and regulations. We scored notable achievements in improving financial governance, hit our poverty alleviation targets for the year, and secured fresh progress in improving the environment.
一是重大风险总体可控。宏观杠杆率过快增长势头得到有效遏制,金融市场总体平稳,人民币汇率保持合理稳定,市场约束逐步增强,审慎经营理念得到强化,金融监管制度进一步完善,金融乱象整治取得阶段性成效。稳步推进外债登记制管理改革,有效防范外债风险。重点城市新建商品住宅销售价格上涨态势基本得到控制,因地制宜调整完善棚户区改造的货币化安置政策。
1) Major risks were manageable on the whole.
We have curbed excessively rapid growth of the macro-leverage ratio and maintained general stability in the financial market. The RMB exchange rate has remained generally stable at an appropriate level. Market restraints have been gradually enhanced, and the concept of prudent business operations has taken stronger root. Further improvements were made in financial regulation mechanisms, and initial success was achieved in addressing acute problems in the financial sector. We moved forward with reforms to improve the management system for foreign-debt registration and effectively guarded against foreign debt risks. The growth of commodity housing prices in major cities was basically brought under control, and the policy of providing monetary compensation to people displaced by the rebuilding of run-down urban areas was improved according to local circumstances.
二是精准扶贫精准脱贫有力推进。进一步加大对“三区三州”等深度贫困地区和特殊贫困群体的帮扶力度,易地扶贫搬迁、以工代赈等重点任务扎实推进,产业、就业、教育、健康、生态、金融、网络、文化和旅游等扶贫工作持续深化,贫困地区自我发展能力不断增强。农村贫困人口脱贫1386万人,280万人易地扶贫搬迁建设任务顺利完成,帮扶贫困劳动力实现就业388万人。
2) Targeted poverty alleviation registered strong progress.
We stepped up support and assistance to particular groups affected by poverty and to extremely poor areas, including the three regions and three prefectures. We made solid progress in relocating people from inhospitable areas and implementing work-relief programs. We stepped up initiatives to alleviate poverty through the development of local industries, employment, education, healthcare services, culture, tourism, and the internet, as well as the provision of ecological conservation subsidies and financial support. These efforts have enabled poor areas to boost their capacity for self-sufficient development. Over the year, 13.86 million people in rural areas were lifted out of poverty, our target of relocating 2.8 million people from inhospitable areas was achieved, and we helped 3.88 million people in poverty find jobs.
三是污染防治攻坚战取得重大进展。深入贯彻习近平生态文明思想和全国生态环境保护大会精神,全面加强生态环境保护的顶层设计进一步完善,中央生态环境保护督察“回头看”有序开展,河长制湖长制全面建立,国家公园体制试点稳步推进。蓝天、碧水、净土保卫战全面推进,打赢蓝天保卫战三年行动计划等出台实施,细颗粒物(PM2.5)未达标地级及以上城市年均浓度下降10.4%,水、土壤污染防治行动深入开展,主要污染物排放总量和单位国内生产总值二氧化碳排放量进一步下降。坚定不移推进禁止洋垃圾入境,全国固体废物进口总量比上年减少46.5%。加快推进垃圾分类处理。初步划定京津冀等15个省份生态保护红线,山西等16个省份基本形成划定方案。深化生态环境保护综合行政执法改革的指导意见印发实施。重大生态保护修复工程有序推进。实施退耕还林还草1238万亩,实施草原围栏、退化草原改良等退牧还草工程3700多万亩。加强滨海湿地保护、严格管控围填海。市场化、多元化生态保护补偿机制建设积极推进,创新和完善促进绿色发展价格机制的意见出台实施。北方地区冬季清洁取暖工作稳妥推进,天然气产供储销体系建设取得积极进展。重点地区煤炭消费减量替代持续推进,用能权交易试点启动实施,提前两年完成燃煤电厂超低排放和节能改造总量目标任务,清洁能源消纳长效机制建设和运行调节加强,弃电量和弃电率实现“双降”,单位国内生产总值能耗下降3.1%。全国碳排放权交易市场建设稳步推进。推动联合国气候变化大会取得积极成果,为《巴黎协定》实施细则的通过发挥重要作用。
3) Major progress was made in the critical battle against pollution.
Putting into practice Xi Jinping’s thinking on promoting ecological progress and the principles from the national conference on ecological and environmental protection, we improved top-level planning for strengthening ecological and environmental protection across the board. Follow-up environmental inspections were carried out by the central government as planned, the river chief and lake chief systems came into effect nationwide, and trials of the national park system registered steady progress.
We launched campaigns to protect our blue skies, clear waters, and clean lands across the country and began implementing the Three-Year Action Plan for Keeping Our Skies Blue. The annual average concentrations of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) decreased by 10.4% in the cities at and above prefecture level that fell short of the national standards, and further steps were taken to address water and soil pollution. Total emissions of major pollutants and carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP continued to fall.
We took resolute measures to block illegal waste imports, and achieved a reduction of 46.5% in solid waste imports on the previous year. Work on the sorted treatment of waste made rapid progress. We completed the first steps in setting standards for enforcing ecological-conservation red lines in 15 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities, including Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, and basically completed plans for 16 others including Shanxi. We formulated the guidelines on deepening reforms for coordinated administrative law enforcement to protect ecosystems and the environment.
We made steady progress in major ecological conservation and restoration projects. We returned more than 825,333 hectares of marginal farmland to forest or grassland, and undertook projects to return 2.47 million hectares of grazing land to grassland, which involved constructing grassland fencing and improving the condition of degraded grasslands. We did more to protect coastal wetlands and strictly controlled and regulated coastal reclamation activities. Progress was made in establishing market-based mechanisms for diversified ecological compensation and the Guidelines on Innovating and Improving Pricing Mechanisms for Promoting Green Development were issued for implementation.
We steadily moved forward with the work to adopt clean energy sources for winter heating in northern China, and achieved progress in building systems for natural gas production, supply, reserve, and sale. We continued working to cut coal consumption and to replace coal with alternative energy in key areas, and launched trials on trading energy consumption rights. The total volume targets for upgrading coal-burning power plants nationwide to achieve ultra-low emissions and energy efficiency were completed two years ahead of schedule. We made moves to strengthen the development and regulation of the long-term mechanism for absorbing clean energy into power grids, and delivered a reduction in both the amount and ratio of idle power and a decrease of 3.1% in energy consumption per unit of GDP. Steady progress was made in establishing a national market for trading carbon emission rights.
On the international stage, China worked to bring about positive results at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Poland, and made an important contribution to ensuring the adoption of the Paris Agreement’s implementation guidelines.
(四)全面实施创新驱动发展战略,创新创业活力持续释放。强化创新第一动力作用,科技体制改革取得实质性突破,国家创新体系效能大幅提升,高技术产业和战略性新兴产业实现较快发展,“互联网+”行动深入推进,新动能培育取得积极进展,创新创业水平进一步提高,创新型国家建设迈出新步伐。
4. We fully implemented the innovation-driven development strategy and continued to unlock new enthusiasm for innovation and business startups.
We bolstered the role of innovation as the primary driver of development. Substantive breakthroughs were made in reforming the management system for science and technology, and efficiency was greatly enhanced in the national innovation system. High-tech industries and strategic emerging industries recorded rapid growth, the Internet Plus action plan was further implemented, and much progress was made toward fostering new growth drivers. Innovation and business startups have been elevated to yet higher levels, and new strides have been made in building China into a country of innovators.
一是科技实力和创新能力不断提升。全国研究与试验发展经费投入强度达到2.18%,科技进步贡献率预计提高到58.5%。基础研究进一步加强,首次在半导体量子点体系中实现三量子比特逻辑门,首次发现铁基超导体中的马约拉纳束缚态,首次人工创建单条染色体真核细胞。一批重大科技成果涌现,嫦娥四号探测器成功着陆月球背面,第二艘航母出海试航,国产大型水陆两栖飞机水上首飞,北斗导航系统面向全球开启服务,5G技术系统设备达到预商用水平。重大科技、民用空间、信息等领域基础设施建设提质提速,科研管理机制和评价激励制度不断完善。全面创新改革试验169项先行先试改革举措已完成123项,第二批共23项改革举措正在复制推广。北京、上海全球影响力科技创新中心建设加速推进,粤港澳大湾区国际科技创新中心建设方案印发实施,北京怀柔、上海张江、安徽合肥3个综合性国家科学中心建设进展顺利,海南省创新驱动发展战略实施方案出台实施。国家级新区、开发区和20个国家自主创新示范区、168个国家高新区的引领作用增强,高速列车、新能源汽车等国家技术创新中心建设深入推进。国家产业创新中心工作指引出台实施,先进计算、先进存储、生物育种等3个国家产业创新中心加快建设。企业技术创新主体地位不断提高,新认定111家国家企业技术中心。
1) Our scientific and technological strength and innovation capacity continued to increase.
China’s spending on R&D reached 2.18% of GDP, and the contribution of scientific and technological advances to economic growth hit 58.5%. Basic research was further strengthened with a number of firsts being achieved: Chinese scientists demonstrated a toffoli gate in a semiconductor three-qubit system, found evidence for Majorana bound states in an iron-based superconductor, and created a single-chromosome eukaryote. We also saw a constant stream of major scientific and technological advances throughout the year: The Chang’e-4 lunar probe successfully landed on the far side of the moon; China’s second homemade aircraft carrier took to the seas for its trial voyage; our homemade large amphibious aircraft completed its first overwater flight; the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System began providing services to the world; and China’s 5G system equipment has reached the pre-commercial level.
We ensured faster and better-quality infrastructure construction in major science and technology, civil-space, information, and other fields, and continued improving the management mechanisms and assessment and incentive systems for scientific research. Pilot reforms for comprehensive innovation have made further progress – 123 out of 169 preliminary trials were completed and a second batch of 23 reform measures are currently being replicated and applied on a broader scale. Efforts to see Beijing and Shanghai become global science and technology innovation centers picked up pace, plans on building Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area into an international center for science and technology innovation were issued for implementation, and construction on the three comprehensive national science centers in Beijing’s Huairou, Shanghai’s Zhangjiang, and Anhui’s Hefei advanced smoothly. The Implementation Plan for the Innovation-Driven Development Strategy of Hainan Province was released.
Our state-level new areas, development zones, 20 national innovation demonstration zones, and 168 national new- and high-tech development zones played a stronger role in leading development, and good progress was made in the construction of national technological innovation centers for high-speed trains and NEVs. We unveiled the Guidelines on Building National Industrial Innovation Centers, and stepped up the building of the three national industrial innovation centers for advanced computing, advanced memory technology, and bio-breeding. We continued to enhance the role of enterprises as the principal entities in technological innovation, and certified a further 111 state-level enterprise technology centers.
二是大众创业万众创新纵深推进。推动创新创业高质量发展打造“双创”升级版的意见出台实施,制造业“双创”平台培育三年行动计划深入推进,确定150个制造业“双创”平台试点示范项目。6500多家众创空间服务创业团队40万家,创业就业人数超过140万人。1824家星创天地培训农村创业人才4.9万人次,孵化企业2.3万家。加强“双创”示范基地建设和小微企业创业创新示范基地建设,建立完善国家创新创业政策信息服务网,成功举办2018年全国“双创”活动周和“创响中国”系列活动。国家新兴产业创业投资引导基金有效运转,新投资企业超过1200家。全年新登记注册企业增长10.3%,平均每天新设1.84万户。
2) Business startups and innovation initiatives were intensified.
The Guidelines on Promoting High-Quality Development of Innovation and Business Startups and Upgrading the National Business Startups and Innovation Initiative was promulgated. We continued to carry out the Three-Year Action Plan for Developing Business Startups and Innovation Platforms in Manufacturing, and confirmed 150 demonstration projects to pilot these platforms. Over 6,500 maker spaces have served 400,000 entrepreneurial teams, and helped generate over 1.4 million jobs; 1,824 rural maker spaces have filled 49,000 places on training courses and incubated 23,000 enterprises. We encouraged more robust development of business startups and innovation demonstration centers and similar demonstration hubs for small and micro businesses, and set up a sound national information service portal for related policies. We successfully held the 2018 National Entrepreneurship and Innovation Week and the Innovating China Tour. The National Venture Capital Guide Fund for Emerging Industries operated effectively, helping more than 1,200 new enterprises receive investment. The number of newly registered businesses in 2018 grew by 10.3%, with an average of 18,400 new businesses daily.
三是新兴产业蓬勃发展。全面落实“十三五”国家战略性新兴产业发展规划,推动战略性产业集群发展,“互联网+”、新一代信息基础设施、人工智能创新发展、生物产业倍增、民用空间基础设施等重大工程加速推进。规模以上高技术制造业增加值增长11.7%,快于全部规模以上工业增速。电子商务法正式公布,引导和规范数字经济、共享经济等新业态健康发展的政策文件陆续出台,对新业态新模式的包容审慎监管进一步完善,智能零售、产能共享等新热点持续涌现,全年实物商品网上零售额增长25.4%,占社会消费品零售总额比例达18.4%,比上年提高3.4个百分点。京津冀、贵州等8个国家大数据综合试验区加快建设。
3) Emerging industries enjoyed vigorous development.
The National Development Plan for Strategic Emerging Industries during the 13th Five-Year Plan Period was fully implemented. We promoted the development of strategic industry clusters, and moved faster to advance major projects on the “Internet Plus” model, next-generation information infrastructure, innovation-driven AI development, bio-tech industry, and civil-space infrastructure. The value-added of large high-tech manufacturing enterprises grew 11.7%, much higher than that of large industrial enterprises as a whole. The E-Commerce Law was promulgated, and a number of policies were issued over the course of the year to guide and regulate the development of new forms of business, such as the digital economy and the sharing economy. Accommodative and prudential regulation over new industries and new forms of business was further improved, allowing for the emergence of a stream of new hot innovations such as smart retail and capacity sharing. The online retail sales of goods grew by 25.4%, accounting for 18.4% of total retail sales of consumer goods, an increase of 3.4 percentage points from the previous year. We accelerated the building of eight national comprehensive experimental zones for big data in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, Guizhou, and other areas.
四是军民融合发展战略扎实推进。国家军民融合创新示范区启动建设。科技军民融合重点专项与军民科技协同创新平台启动,军民融合重大示范项目建设进展顺利。国家军民融合信息化平台建设有力推进。国家国防科技工业军民融合产业投资基金、国家级军民融合发展产业投资基金启动运行。支持符合条件的军民融合企业发行企业债券,拓宽军民融合投融资渠道。第三届中国军民两用技术创新应用大赛和第四届军民融合高技术装备成果展成功举办。
4) The military-civilian integration strategy was implemented to good effect.
Construction began on demonstration zones to promote innovation in military-civilian integration (MCI). Key special MCI projects on science and technology and the platform for military-civilian collaborative innovation in science and technology were launched. Smooth progress was made in major MCI demonstration projects, and strong steps were taken to develop the national MCI information platform. The national MCI industrial investment fund for defense-related science, technology, and industry was put into operation, along with the national-level MCI industrial investment fund. We also broadened investment and financing channels for military-civilian integration, by offering support for qualified MCI enterprises to issue corporate bonds. The third China Dual-Use Technology and Application Contest and the fourth Exhibition of MCI High-Tech Equipment Outcomes were successfully held.
(五)深化改革扩大开放,经济社会发展动力进一步激发。按照深化党和国家机构改革方案,国务院机构改革有序推进。深入开展纪念改革开放40周年系列庆祝活动,推动一系列重大改革开放举措落地。
5. We pursued deeper reform and greater opening-up and unlocked more drivers of economic and social development.
Reform of the State Council’s institutions progressed as per the arrangements in the Plan on Deepening Reform of Party and State Institutions. A vast array of activities were held to celebrate the 40th anniversary of China’s reform and opening-up, and a host of major measures to promote reform and opening-up were implemented.
一是营商环境持续优化。“放管服”改革深入推进。全面实施全国统一的市场准入负面清单制度,市场准入负面清单(2018年版)发布,清单以外的行业、领域、业务等各类市场主体皆可依法平等进入。取消汽车投资项目核准等一批行政许可事项,大幅压缩企业开办时间,副省级以上城市和省会城市企业开办时间压缩至8.5个工作日以内。“证照分离”改革在全国推开,全面实施全国统一“二十四证合一”改革。工业产品生产许可证制度改革加快推进,产品种类由38类降至24类。在北京等15个城市和浙江省开展工程建设项目审批制度改革试点。世界银行公布的我国营商环境全球排名由2017年第78位大幅跃升至第46位。在22个城市开展中国营商环境试评价,中国营商环境评价体系初步构建。深入推进“双随机、一公开”监管,基本实现市场监管领域日常监管全覆盖。社会信用体系建设持续推进,电信诈骗、偷逃骗税等19个重点领域失信问题专项治理深入开展,守信联合激励和失信联合惩戒机制初显成效。政务服务“一网一门一次”改革启动实施,建立国务院部门数据共享责任清单,基本建成全国一体化的数据共享交换平台体系,数据共享交换量达360亿条次。深入推进审批服务便民化,“减证便民”行动和“群众办事百项堵点疏解行动”扎实开展。
1) The business environment consistently improved.
Reforms to streamline administration, delegate powers, improve regulation, and upgrade services continued apace. Fully implementing the Negative List for Market Access, we issued the 2018 version, and took steps to ensure industries, sectors, and commercial activities not on the list could be fairly accessed by all types of market entities in accordance with law. We also abolished a number of items subject to administrative approval including those for automobile investment projects. The time taken to set up a business has been dramatically shortened to within 8.5 working days in cities at and above sub-provincial level and provincial capitals.
The reform separating out the business license from certificates required for starting a business was rolled out nationwide, and the national reform to merge 24 types of certification into one certificate was fully implemented. Reform of the industrial production licensing system picked up speed, and the number of product categories has been cut from 38 to 24. Trial reforms on the approval system for construction projects were started in Beijing and 14 other cities, as well as in Zhejiang Province. In the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business ranking (2019), China jumped from 78th to 46th place. We also piloted a business environment evaluation suited to China’s conditions in 22 cities, marking the first step toward establishing China’s own business environment evaluation system.
Progress was made in promoting the oversight model using randomly selected inspectors to inspect randomly selected entities and requiring the prompt release of results, and full coverage of daily oversight in market regulation was basically realized. We continued building the social credit system. We introduced targeted measures in 19 key sectors against acts in bad faith, including telecom fraud, tax evasion, and tax fraud. The mechanisms of joint incentives for acts of good faith and joint punishment for acts of bad faith produced initial results.
We launched reforms to see that people need only log in to one website or visit one place and make one trip to access a government service. We formulated lists of responsibilities on data sharing for departments under the State Council, and basically established a national unified system of platforms for sharing and exchanging data. This system has so far facilitated data exchanges of 36 billion in number. We worked hard to provide more convenient approval services, and made solid progress in the “less certificates, more convenience” initiative and the campaign to free up 100 bottlenecks preventing people from accessing government services.
二是国资国企改革加快推进。国有企业混合所有制改革积极稳步开展,深化混合所有制改革试点有关政策出台实施,三批50家混合所有制改革试点梯次推进并取得重要阶段性成效。改革国有企业工资决定机制的意见、推进国有资本投资、运营公司改革试点的实施意见出台,深化国企改革“1+N”政策体系搭建完成。加强国有企业资产负债约束的指导意见印发实施,国有企业资产负债约束机制初步建立。中国特色现代国有企业制度进一步完善,有效制衡的法人治理结构和灵活高效的市场化经营机制加快建立。
2) Reform of state capital and SOEs picked up pace.
The reform to introduce mixed ownership to SOEs moved forward in an active and steady manner. We issued the policies for deepening pilot reforms on mixed ownership, and carried out pilot mixed-ownership reforms sequentially in 50 SOEs in three groups, yielding important results. The Guidelines on Reforming the Salary-Setting Mechanism for SOEs and the Guidelines on Promoting Pilot Reforms in State Capital Investment and Management Companies were published. A system anchored by the Guidelines on Deepening Reform of SOEs as well as other supplementary policies was put in place. The Guidelines on Strengthening Constraints on SOEs’ Debt-to-Asset Ratios were promulgated, marking the initial step in setting up a constraint mechanism for SOEs’ debt-to-asset ratios. The modern SOE system with Chinese characteristics was further improved, and faster progress was made in establishing a corporate governance structure with effective checks and balances and flexible and efficient market-based operating mechanisms.
三是支持民营经济发展力度加大。加强产权和知识产权保护,建立健全产权保护协调机制,全面清理涉及产权保护的规章规范性文件,深入开展政府机构失信问题专项治理行动。“互联网+”知识产权保护工作方案出台实施。大力弘扬企业家精神,私营企业暂行条例废止。着力疏通货币政策传导机制,鼓励金融机构扩大对实体经济特别是制造业企业、民营企业、小微企业的信贷投放。设立民营企业债券融资支持工具,以市场化方式帮助企业缓解融资难问题。
3) The private sector received stronger support.
We strengthened the protection of property rights and intellectual property rights (IPR). We set up a robust mechanism to ensure coordinated property rights protection, conducted a review of all regulations and normative documents relating to property rights protection, and carried out extensive campaigns to address failures within government institutions to act in good faith in this area. The Plan for the Internet Plus IPR Protection was unveiled. In line with our efforts to promote entrepreneurship, we repealed the Provisional Regulations for Private Enterprises. We worked to improve the transmission mechanism of monetary policy, and encouraged financial institutions to provide more credit to the real economy and to manufacturing firms, private enterprises, and small and micro businesses in particular. We set up instruments to support private enterprises in debt financing and help them find market-based solutions to financing problems.
四是财税金融改革稳步推进。中央与地方财政事权和支出责任划分改革分领域推进,预算绩效管理制度不断完善。增值税改革进一步深化。修改个人所得税法及其实施条例,提高基本减除费用标准,设立6项专项附加扣除,税率结构进一步调整优化。环境保护税顺利开征。完善系统重要性金融机构监管、加强非金融企业投资金融机构监管、完善国有金融资本管理等政策文件出台实施。有序推动民营银行发展,17家民营银行获批开业。
4) The reform of the fiscal, tax, and financial systems registered steady progress.
We continued reforms to divide fiscal powers and expenditure responsibilities between central and local governments on a sector by sector basis, and made consistent improvements to performance-based budgetary management. In the area of tax, further progress was made in VAT reform. We revised the Law on Individual Income Tax and its implementation regulations, raised the income tax threshold, introduced six special deductible items, and improved the structure of tax rates. The environmental protection tax came into force.
We published policies on improving regulation of systemically important financial institutions, on strengthening oversight over nonfinancial firms’ investment in financial institutions, and on improving the management of state-owned financial capital. The orderly development of private banks was promoted, with approval being granted for the establishment of 17 private banks.
五是共建“一带一路”取得新进展。推进“一带一路”建设工作5周年座谈会召开,为推动“一带一路”建设走深走实明确了方向。围绕重点方向重点国别,巩固共建意愿、推动规划对接,已累计同150多个国家和国际组织签署171份政府间合作文件。国际产能合作稳步推进,境外经贸合作区产业集聚效应增强,与法国、日本、新加坡等10多个国家签署第三方市场合作文件,中老、中泰铁路和中阿(联酋)“一带一路”产能合作园区等重点项目取得实质性进展,雅万高铁全面开工,瓜达尔港等重点港口项目进展顺利,中欧班列提质增效工作取得重要进展,累计开行超过1.3万列,回程率提高近20个百分点。“一带一路”沿线国家航空互联互通水平显著提高,新开航线106条。“一带一路”国际科学组织联盟成立,推动与东盟、南亚、阿拉伯国家、中亚、中东欧5个区域共建技术转移平台,推动与菲律宾、印尼等8个国家共建科技园区。中非合作论坛北京峰会取得圆满成功和丰硕成果。数字丝绸之路建设稳步推进,已与16个国家签署合作谅解备忘录,“丝路电商”全球布局步伐加快,与17个国家签署合作协议。
5) The Belt and Road Initiative made new advances.
A symposium was held to mark the fifth anniversary of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). During the symposium the BRI’s future trajectory was outlined with a view to ensuring it continues building momentum and producing concrete outcomes. Focusing on key areas and key countries, we worked to build on the collective desire for cooperation and promoted the coordination of development plans. To date, a total of 171 inter-governmental cooperation documents have been signed with over 150 countries and international organizations.
We steadily increased international industrial-capacity cooperation. The positive effect of industrial concentration in overseas economic and trade cooperation zones was much more noticeable, and third-market cooperation documents were signed with over ten countries, including France, Japan, and Singapore. There was substantial progress in key BRI projects like the China-Laos and China-Thailand rail lines and the China-UAE Industrial Park. Construction is fully underway on the Jakarta-Bandung high-speed line and making smooth progress on key port projects like Gwadar in Pakistan. We made important improvements to the quality and efficiency of the China-Europe freight train services. The services have so far registered over 13,000 trips, and have seen a 20-percentage-point increase in the number of return journeys to China. Marked progress was made in aviation connectivity among BRI countries, with the opening of 106 new air routes.
The BRI International Science Organizations Alliance was established to promote collaboration on building technology transfer platforms between China and ASEAN, Arab states, and countries in south Asia, central Asia, and central and eastern Europe, and to co-establish science and technology parks with the Philippines, Indonesia, and six other countries. We successfully hosted the Beijing Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, which produced many positive outcomes. Work on the Digital Silk Road progressed steadily with the signing of cooperation MOUs with 16 countries, and faster moves were made to promote Silk Road E-Commerce across the globe with the signing of cooperation agreements with 17 countries.
六是贸易强国建设扎实推进。首届中国国际进口博览会成功举办,向全世界宣示了我国主动开放市场、推动经济全球化的决心。区域全面经济伙伴关系协定谈判加速推进,与新加坡签署自贸协定升级版,与毛里求斯完成自贸协定谈判,累计已与25个国家和地区达成17个自贸协定,多双边经贸合作进一步深化。出台53项措施支持自贸试验区深化改革创新,在全国范围内复制推广30项自贸试验区改革试点经验。海南全岛自贸试验区启动建设,探索建设中国特色自由贸易港。新设一批跨境电子商务综合试验区,完善跨境电商零售进口监管和税收政策,扩大市场采购贸易试点范围,跨境电子商务、市场采购贸易等新业态新模式蓬勃发展。关税总水平由9.8%下调至7.5%,积极扩大进口促进对外贸易平衡发展。多元化市场不断拓展,全年货物贸易进出口总额达30.51万亿元,增长9.7%。
6) China made solid progress in developing as a trader of quality.
We successfully hosted the first China International Import Expo, an event which has shown to the world China’s determination to continue opening its market and promote economic globalization. We stepped up negotiations on the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, signed an upgraded free trade agreement (FTA) with Singapore, and completed FTA negotiations with Mauritius. With this, China has further strengthened its bilateral and multilateral economic and trade cooperation, and signed a total of 17 FTAs with 25 countries and regions.
We adopted 53 measures to deepen reform and promote innovation in pilot free trade zones, and applied 30 practices developed from trial reforms in pilot free trade zones across the country. We began work on building China (Hainan) Pilot Free Trade Zone, and carried out exploratory work on setting up free trade ports with Chinese features. We built more integrated experimental zones for cross-border e-commerce, improved retail import supervision and taxation policies on cross-border e-commerce, and expanded the scope of trials on market procurement trade. These steps have helped support the vigorous development of new forms and models of trade such as cross-border e-commerce and market procurement trade. We lowered China’s overall tariff level from 9.8% to 7.5% and worked to balance China’s foreign trade by actively expanding imports. The diversity of China’s market grew continuously. The total value of imported and exported goods for the year stood at 30.51 trillion yuan, an increase of 9.7%.
七是利用外资环境不断优化。全面放宽市场准入,2018年版全国和自贸试验区两个外资准入负面清单发布,特别管理措施分别压减至48条、45条,金融领域对外开放稳步推进。在全国推行外资企业设立商务备案与工商登记“一口办理”,积极推进在产业政策、科技政策、政府采购、资质许可、标准制定等方面平等对待内外资企业,开发区改革和创新发展不断深化,外商投资环境持续优化。全年外商直接投资达1350亿美元,增长3%。
7) The foreign investment environment was continuously improved.
Restrictions on market access were relaxed across the board. Two editions of the 2018 negative list for foreign investment were published, one for the whole country and the other for pilot free trade zones. The number of special administrative measures applying in each case has been reduced to 48 and 45 respectively. Steady progress was made in opening up the financial sector. We instituted a nationwide policy of allowing foreign-invested enterprises to complete business filing procedures and business registration in one go. We took active steps to promote equal treatment of domestic and foreign enterprises in terms of industrial policy, science and technology policy, government procurement, license applications, and standards-setting. Reform and innovation-driven development in development zones were stepped up, and the business environment for foreign investors continued to improve. China attracted around US$ 135 billion in foreign direct investment over the year, an increase of 3%.
八是对外投资平稳有序发展。企业境外投资管理办法、对外投资备案(核准)报告暂行办法正式施行,全口径、全过程管理不断完善,对外投资行业结构进一步优化,主要流向租赁和商务服务业、制造业等。发布企业境外经营合规管理指引,企业合规意识有所增强。引导对外投融资基金健康发展,企业“走出去”融资渠道进一步拓宽。全年非金融类境外直接投资达到1205亿美元。
8) Development of outward investment was steady and orderly.
The Management Provisions for Outward Investment by Enterprises and the Interim Measures for Reporting on the Registration (Approval) of Outward Investment were put into force. We enhanced unified supervision over outward investment at all stages and further improved the sectorial composition of outward investments, with the bulk flowing into leasing, business services, and manufacturing. To enhance the awareness of enterprises about compliance, we published the Guide on Compliance Management for Enterprises’ Overseas Operations. We provided guidance to see the sound development of outward investment and financing funds, thus expanding the channels through which enterprises can seek financing for their “go-global” efforts. Non-financial outward direct investment reached US$ 120.5 billion in 2018.
(六)大力实施乡村振兴战略,农业农村发展新动能加快培育。乡村振兴战略规划(2018-2022年)出台实施,28个省级乡村振兴战略规划已印发,其他省(区、市)已基本完成规划编制工作,多规合一的村庄规划编制部署推进,乡村振兴的制度框架和政策体系逐步建立,乡村振兴阶段性重点工作全面展开。
6. We put strong focus on implementing the rural revitalization strategy and moved faster to foster new growth drivers for agricultural and rural development.
The Strategic Plan for Rural Revitalization (2018-2022) was issued for implementation. A total of 28 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) have already published complimentary plans. In addition, plans for all others have been basically completed, and work on rolling separate village development plans into one single plan has continued. The institutional framework and policy system for rural revitalization have been gradually established and all major work planned for the current stage has begun.
一是农业基础进一步夯实。粮食总产量保持在1.3万亿斤以上。新增高效节水灌溉面积2158万亩,新增高标准农田8000多万亩,完成9亿多亩粮食生产功能区和重要农产品生产保护区划定任务。深入实施现代化种业提升工程,高标准建设国家南繁科研育种基地,加快推动粮油、蔬菜、水果等农作物种子种苗基地建设。172项重大水利工程累计开工133项,在建投资规模超过1万亿元。全年完成营造林2.34亿亩。开展“农业质量年”行动,加快推进质量兴农、绿色兴农、品牌强农,主要农产品质量安全监测合格率保持在97%以上,化肥、农药使用量均下降。
1) The foundations of agriculture grew stronger.
Total grain output exceeded 650 million metric tons. Efficient water-saving irrigation methods were newly applied to 1.44 million hectares of land. The area of high-standard cropland was increased by over 5.33 million hectares. We have established functional zones for grain production and protective areas for the production of major agricultural products on an area of over 60 million hectares. We stepped up the initiative to upgrade the modern seed industry, ensured high standards were adopted in the building of the Nanfan National Seed Breeding Base, and sped up construction on seed and seedling breeding bases for grain and oil-bearing crops, vegetables, and fruits.
Work has begun on 133 of 172 planned major water conservancy projects, with the total investment in ongoing projects exceeding 1 trillion yuan. A total of 15.6 million hectares of land were afforested throughout the year. The Year of Agricultural Quality campaign was carried out to spur agricultural development by raising quality standards, promoting green development, and building strong brands. The percentage of major agricultural products that passed quality and safety tests remained above 97%, and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides both decreased.
二是农村一二三产业融合发展取得积极进展。认定农村产业融合发展示范园100家,启动创建现代农业产业园62个、农业产业强镇254个。深入实施主要农作物生产全程机械化推进行动。大力发展智慧农业,农业生产、经营、管理、服务数字化水平进一步提升。农村新产业新业态加快培育。
2) Development of the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries was much more integrated in rural areas.
A total of 100 demonstration parks for rural industry integration have so far been certified, and work started on building 62 modern agricultural industrial parks and 254 towns with agricultural strengths. We continued promoting complete mechanization of the production process for major crops. We also concentrated on developing intelligent agriculture, boosting the levels of digitization in agricultural production, operations, management, and services. New industries and new forms of business in rural areas enjoyed rapid development.
三是农业农村改革稳步推进。完善稻谷、小麦最低收购价政策制度。健全玉米和大豆市场化收购加补贴机制。农村土地征收、集体经营性建设用地入市、宅基地制度改革试点工作有序推进。宅基地和农房确权登记发证加快实施,土地承包权确权登记颁证工作基本完成,承包地已确权面积14.8亿亩,超过二轮家庭承包地(账面)面积。建立健全进城落户农民土地承包权、宅基地使用权、集体收益分配权维护和自愿有偿退出机制,在3个省、50个地市、150个县启动第三批农村集体产权制度改革试点。全国已有超过15万个农村集体组织完成改革,共确认集体成员2亿多人。集体林权制度改革进一步深化。
3) Agricultural and rural reforms registered steady progress.
We made improvements to the policy on setting minimum purchase prices for wheat and rice and to the mechanism for combining market-based purchases with government subsidies for corn and soybeans. Well-planned steps were taken to push forward with trial reforms on rural land requisition, the marketization of rural collective land designated for business-related construction, and the system for rural land designated for housing. We stepped up work to determine, register, and certify rural home land rights and rural housing property rights, and basically completed the work to determine, register, and certify contracted rural land rights. Rights on 986.7 million hectares of contracted land have been certified, exceeding the cadastral area covered during the second round of household land contracting in rural areas. We have set up robust mechanisms for former rural residents who now hold urban residency to protect their rights on contracted rural land, use rights on rural land designated for housing, and rights to share in the proceeds from rural collective undertakings, as well as their entitlement to voluntarily transfer these rights in return for compensation. The third batch of trials to reform the rural collective property rights system began in 150 counties in 50 prefectures and cities and in 3 provinces. To date, this reform has been completed by over 150,000 rural collectives nationwide and has involved more than 200 million people. Reform of collective forest tenure was furthered.
四是美丽宜居乡村建设步伐加快。农村人居环境整治三年行动全面启动。农村突出环境问题综合治理试点示范和农村生活污水治理示范有序开展。农村生活垃圾治理覆盖面进一步扩大,厕所革命积极推进。农村饮水安全巩固提升工程加快实施,农村自来水普及率进一步提升。农村公路建设加快推进。农村机井通电、小城镇中心村农网改造升级、贫困村通动力电等顺利完成。开展电信普遍服务试点、“宽带乡村”、“百兆乡村”示范工程,新一代信息基础设施建设工程加快推进。农村基层综合性文化服务中心建设有序推进。
4) Work on building a beautiful and livable countryside picked up pace.
The three-year campaign to improve rural living environments got underway across the country. We steadily moved forward pilot demonstration programs to comprehensively address serious environmental problems and demonstrations to treat household wastewater in rural areas. The project to manage household refuse was extended to more rural areas and the Toilet Revolution was actively carried forward. We stepped up efforts to consolidate and build on the progress made in providing safe drinking water, and increased the availability of tap water in rural areas. More rural roads were built. We successfully concluded the projects to provide power to all electric pump sets on rural flatlands, to upgrade power grids in small towns and hub villages, and to provide three-phase power to poor villages. We carried out trials of providing universal telecommunications services and demonstration projects to extend broadband connectivity, and particularly to install 100M fiber optic networks in rural areas, and moved faster to build next-generation information infrastructure there. The orderly development of multipurpose cultural service centers in rural areas continued.
(七)统筹推动区域协调发展,空间发展格局更趋优化。发挥各地区比较优势,努力缩小区域发展差距,大力推进新型城镇化建设,区域发展的协同性、联动性、整体性进一步增强。
7. We took holistic steps to promote coordinated regional development and saw further improvements in spatial development patterns.
We gave play to the comparative advantages of different regions, worked on narrowing regional development disparities, and focused on promoting new urbanization. Stronger levels of coordination, connectivity, and integration were achieved in development between regions.
一是进一步促进区域协调发展。建立更加有效的区域协调发展新机制的意见出台实施。推动西部地区进一步开发开放,新开工交通、能源等重点工程28项,总投资4825亿元。东北地区营商环境建设、民营经济发展、与东部对口合作等取得新突破,老工业城市和资源型地区转型稳步推进,城区老工业区、独立工矿区改造搬迁和采煤沉陷区综合治理持续实施。先进制造业在中部地区合理布局提速,汉江、淮河生态经济带发展规划以及湘南湘西承接产业转移示范区总体方案出台实施。东部地区新动能加快培育壮大,组织开展山东新旧动能转换综合试验区建设。革命老区、民族地区、边疆地区、贫困地区加快发展,交通、水利、能源、通信、物流等重大基础设施建设扎实推进,对口支援深入开展,支持新疆、西藏和四省藏区经济社会发展政策措施进一步完善。海洋经济发展示范区启动建设,海洋强国建设加快推进。国家级新区、临空经济示范区、综合配套改革试验区等功能平台的示范引领作用不断增强。沿边重点开发开放试验区建设稳步推进,形成了一批可复制可推广经验。
1) Further strides were made in promoting coordinated regional development.
The Guidelines on Establishing More Effective New Mechanisms for Coordinated Regional Development were released. To promote further development and opening-up in the western region, we launched 28 major projects in transportation, energy, and other fields with a total investment of 482.5 billion yuan. In the northeast, breakthroughs were made in improving the business environment, developing the private sector, and promoting cooperative partnerships with the eastern region; steady progress was made in the transformation of old industrial cities and resource-dependent areas; efforts were continued to rebuild or relocate old industrial districts within cities and independent industrial and mining areas and to implement comprehensive solutions in areas affected by mining-induced subsidence. In the central region, we moved faster to achieve a rational distribution of advanced manufacturing, and began to implement development plans for the Han and Huai river eco-economic belts and the general plan for industrial relocation demonstration zones in southern and western Hunan. The eastern region moved faster to foster and strengthen new growth drivers; in Shandong, work began on a comprehensive experimental zone for replacing old growth drivers with new ones.
Old revolutionary base areas, areas with large ethnic minority populations, border areas, and poor areas all recorded faster development, achieving solid progress in constructing major infrastructure such as transportation, water conservancy, energy, communications, and logistics facilities. We scaled up one-to-one assistance programs, and further improved economic and social policies and measures in Xinjiang, Tibet, and the Tibetan ethnic areas in Sichuan, Yunnan, Gansu, and Qinghai provinces.
We took faster steps toward building China into a strong maritime country, with construction beginning on demonstration zones for developing the marine economy. Many functional platforms, such as state-level new areas, airport economy demonstration zones, and experimental zones for integrated, complete reform, strengthened their ability to demonstrate and offer guidance on reform practices. Steady progress was made in the construction of experimental zones for development and opening-up in major border areas, giving rise to a set of practices applicable to other areas.
二是重大区域发展战略有力推进。以疏解北京非首都功能为“牛鼻子”,推动京津冀协同发展取得明显进展,河北雄安新区规划纲要、支持河北雄安新区全面深化改革和扩大开放的指导意见、河北雄安新区总体规划(2018-2035年)出台实施,北京城市副中心规划建设提速,京雄城际铁路开工建设,北京大兴国际机场建设和运营筹备工作全面推进。长江经济带共抓大保护格局进一步巩固,国土空间规划编制工作启动,“三水共治”、河湖清“四乱”专项行动扎实推进,1361座非法码头专项整治全面完成,长江干流断面水质优良比例明显提高。综合立体交通走廊建设加快推进,沿江高铁规划建设、省际待贯通路段建设提速、长江深水航道建设及干线港口铁水联运取得积极进展。粤港澳大湾区发展规划纲要发布实施,重点项目建设全面启动,港珠澳大桥正式开通运营,一系列便利港澳居民在内地发展的政策举措落地见效。支持海南全面深化改革开放的指导意见出台实施。长江三角洲区域一体化发展规划纲要启动编制。
2) Strong progress was recorded in implementing major regional development strategies.
With the focus on relieving Beijing of functions nonessential to its role as the capital, we made marked progress in promoting the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The Plan for Xiongan New Area in Hebei, the Guidelines on Supporting Xiongan New Area in Comprehensively Deepening Reform and Opening-up, and the General Plan for Xiongan New Area in Hebei (2018-2035) were unveiled for implementation. We sped up the development of the administrative center of Beijing Municipality, began construction on the Beijing-Xiongan Intercity Railway, and made progress on all fronts in building Beijing Daxing International Airport and preparing for its operation.
On the Yangtze Economic Belt, the pattern of close coordination on environmental protection was consolidated. We began formulating a territorial space plan, and made solid progress in employing the three-fold approach of controlling water pollution, restoring water ecosystems, and conserving water resources and in addressing four kinds of behaviors detrimental to environmental protection on rivers and lakes. Rectification work was completed on 1,361 illegal wharves, and the cross-section water quality of the main stream of the Yangtze River improved significantly. Work on the integrated multidimensional transportation corridor was stepped up. We made good progress in planning and building a high-speed railway along the Yangtze River, accelerating work on the unfinished sections of inter-provincial expressways, constructing a deep-water channel on the Yangtze, and installing combined rail-water transportation facilities at ports along its main channel.
We unveiled the Development Plan for Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, and initiated major construction projects across the board. The Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge was officially opened to traffic. Policies and measures to make it easier for Hong Kong and Macao residents to pursue development on the mainland came into effect and are producing positive results.
We implemented the Guidelines on Supporting Hainan in Comprehensively Deepening Reform and Opening-Up. Work began on drawing up a plan for integrated regional development of the Yangtze River Delta.
三是新型城镇化质量有效提升。农业转移人口进城落户更加便捷,大中城市落户政策持续放宽,居住证制度全覆盖目标基本实现,全国常住人口城镇化率达59.58%,户籍人口城镇化率达43.37%,比上年末分别提高1.06个百分点和1.02个百分点。一批跨省(区、市)城市群规划出台实施,各地城市群建设全面推进,现代化都市圈加快培育发展。
3) The quality of new urbanization was enhanced.
Rural household registration holders living in urban areas can now obtain permanent urban residency with greater ease. Permanent residency policies continued to be loosened in large and medium-sized cities, and the residence card system was basically implemented in all cities. The percentage of permanent urban residents reached 59.58%, while the percentage of registered urban residents reached 43.37%, 1.06 and 1.02 percentage points above the figures at year-end 2017 respectively. A group of plans for trans-provincial city clusters were published, city clusters throughout the country showed strong development, and modern metropolitan areas grew rapidly.
(八)着力保障和改善民生,发展成果更多更公平惠及人民群众。坚持以人民为中心的发展思想,紧紧围绕人民群众普遍关心的突出问题,推动一大批惠民举措落细落实。
8. We focused on ensuring and improving the people’s wellbeing and saw they enjoyed more of the fruits of development in a fairer way.
Upholding our vision of people-centered development, we pushed for detailed and effective implementation of a whole raft of initiatives aimed at benefiting the people and addressing prominent problems of public concern.
一是稳定就业有序推进。做好当前和今后一个时期促进就业工作的若干意见、推行终身职业技能培训制度的意见出台实施。公共就业创业服务持续加强,援企稳岗力度加大,支持农民工等人员返乡创业试点工作持续推进。高校毕业生就业创业促进计划等深入实施。制定出台推进全方位公共就业服务指导意见,“互联网+公共就业服务”全面推进。人力资源市场暂行条例发布实施,人力资源市场体系逐步健全。
1) Well-planned steps were taken to keep employment stable.
The Guidelines on Promoting Employment for the Present and Coming Period and the Guidelines on Implementing the Life-Long Vocational Skills Training System were promulgated. We enhanced public employment and business startup services, stepped up support for enterprises to keep employment stable, and continued the pilot projects to support rural migrant workers and others returning home to set up businesses. Programs to guide college graduates in finding jobs and starting businesses also continued. We formulated and unveiled the Guidelines on Providing Extensive Public Employment Services, and made impressive strides in instituting the Internet Plus Public Employment Services model. We introduced the Provisional Regulations on Human Resource Markets, thus opening the way for the gradual establishment of a robust HR market system.
二是社会保障制度日益完善。企业职工基本养老保险基金中央调剂制度正式实施,城乡居民基本养老保险待遇确定和基础养老金正常调整机制建立。统一社保费征收管理机构工作稳步推进,社保费征收管理制度进一步规范。整合城乡居民基本医疗保险制度持续推进。养老保险覆盖人数已超过9.42亿人,基本医疗保险覆盖人数已超过13.44亿人。国家跨省异地就医结算平台进一步完善,跨省定点医疗机构实现县级行政区全覆盖,外出农民工、外来就业创业人员全部纳入覆盖范围,异地就医直接结算累计达152.6万人次。生育保险与职工医保合并实施试点稳步推进。失业保险“保生活、防失业、促就业”功能不断完善。农民工参加工伤保险政策进一步健全。低保制度不断完善,城乡低保实现全覆盖且保障水平持续提高。退役士兵就业安置进一步加强,带病回乡退伍军人、参战参试退役人员等优抚对象生活补助标准提高。社会福利服务体系建设加强,社会救助综合改革试点有序开展。城镇保障性安居工程建设扎实推进,城镇棚户区住房改造开工达626万套,公租房新增分配100万套,大中城市住房租赁市场加快培育。农村危房改造190万户。
2) Improvements were made to the social security system on a continuing basis.
The central regulation system for enterprise employees’ basic old-age insurance funds formally came into operation. Mechanisms were established to set standards on benefits for rural and non-working urban residents under the basic old-age insurance scheme and to allow for regular adjustment of their basic pension benefits. Steady strides were made in bringing the tasks of collecting and managing social insurance premiums under the remit of a single agency, and regulation in this area was further improved. We continued to make progress in aligning basic medical insurance schemes for rural residents and non-working urban residents. In total, more than 942 million people are now covered by basic old-age insurance schemes, and over 1.344 billion people are covered by basic medical insurance plans.
We improved the national platform for trans-provincial settlement of medical bills through basic medical insurance accounts. We have ensured there are hospitals designated for trans-provincial settlement in all county-level administrative areas, and have seen that rural migrant workers and other workers and business owners without local residency have been incorporated into the platform. The total number of trans-provincial on-the-spot settlements has reached 1.526 million.
Smooth progress was made in the pilot program in integrating maternity insurance and basic medical insurance for urban workers. Unemployment insurance functioned more effectively in terms of ensuring basic living standards, preventing job losses, and promoting employment. Improvements were made to the policies regarding rural migrant workers’ participation in workers’ compensation schemes. The subsistence allowance system continued to improve as we achieved full coverage for urban and rural residents and ensured continuous improvements in allowance standards.
More was done to assist demobilized military personnel in finding employment, and living allowances were raised for demobilized personnel with illness, for war and nuclear-test veterans, and for other entitled groups. The social welfare services system was strengthened, and trials for integrated reforms in social assistance were pushed forward. Steady progress was made in the construction of government-subsidized housing in urban areas, and renovations began on 6.26 million units of housing in run-down urban areas, and an additional 1 million units of public-rented housing were allocated. The housing rental market developed rapidly in large and medium-sized cities. A total of 1.9 million dilapidated houses in rural areas were renovated.
三是基本公共服务标准体系加快构建。建立健全基本公共服务标准体系的指导意见出台实施,基本公共服务省级清单实现全覆盖。教育现代化推进、全民健康保障、文化旅游提升、公共体育普及、社会服务兜底五大公共服务工程大力推进。九年义务教育巩固率达94.2%,高中阶段教育毛入学率达88.8%,财政性教育经费支出占国内生产总值比例继续超过4%。“互联网+医疗健康”快速发展,公立医院综合改革继续深化,国家基本药物制度进一步完善,药品集中采购和使用试点稳妥推进,境外上市新药审评审批加快,进口抗癌药全部实现零关税,17种抗癌药大幅降价并纳入医保报销目录,疫苗药品安全问题加快解决。每千人口医疗卫生机构床位数预计达6.05张。加强文物保护利用改革的若干意见印发实施,各类遗产资源保护状态得到有效改善。大运河文化保护传承利用规划纲要编制完成。公共文化设施免费开放工作持续开展,百万公里健身步道工程实施方案出台,新增体育场地8.2万个。社会兜底保障加强,困难残疾人生活补贴制度惠及940万人,1164万重度残疾人享受护理补贴。孤儿保障制度惠及39.8万孤儿,为全国残疾孤儿实施医疗康复。持续开展孕期优生优育服务,妇女关爱服务体系不断健全。公共法律服务体系继续完善。全年出生人口1523万人,年末总人口达13.95亿人,人口自然增长率为3.81‰。
3) Development of a system of standards for basic public services progressed quickly.
The Guidelines on Establishing a Sound System of Standards for Basic Public Services were unveiled, and all provincial-level governments released basic public service lists. Strong progress was made in the five major public service categories of modernizing education, ensuring a healthy population, elevating culture and tourism, promoting fitness among the public, and providing social services for groups that are most in need.
The retention rate of nine-year compulsory education hit 94.2%, and the gross enrollment ratio for senior secondary education reached 88.8%. Government spending on education as a percentage of GDP remained above 4%.
We made rapid progress in developing the Internet Plus Medical and Healthcare model, and stepped up the comprehensive public hospital reform. The national system of essential medicines was improved. Trials for centralizing the procurement and use of medicines made steady progress, and the time it takes to assess and approve new drugs coming into the Chinese market was cut. A zero-tariff policy was applied to all imported cancer treatment drugs, while 17 types of cancer treatment drugs were made available at much lower prices and their costs can now be reimbursed through medical insurance. More measures were quickly taken to address problems pertaining to the safety of vaccines and medicines. The number of beds in medical and healthcare institutions is predicted to have reached 6.05 per 1,000 people.
The Guidelines on the Reform to Better Protect Cultural Relics and Put Them to Better Use were published, and the protection for cultural heritage of all types markedly improved. The Plan for Protecting, Passing On, and Utilizing Grand Canal Culture was drawn up. We continued working to offer free access to more public cultural facilities, unveiled an implementation plan for the initiative to build one million kilometers of fitness walkways, and opened 82,000 new sports venues.
We strengthened social security programs to meet basic needs. A total of 9.4 million people with disabilities facing financial difficulties received living allowances, and 11.64 million people with serious disabilities received nursing care subsidies. Around 398,000 children benefited from the subsistence allowance system for orphans, and medical rehabilitation services were provided to orphaned children with disabilities around the country. Better pre- and post-natal care services were ensured, and the support and care system for women was improved. The public legal service system also continued to improve. A total of 15.23 million babies were born in 2018, bringing the total population at year end to 1.395 billion. The natural population growth rate was 3.81‰.
总的来看,2018年经济社会发展主要目标任务较好完成,三大攻坚战开局良好,供给侧结构性改革深入推进,改革开放力度加大,人民生活持续改善,保持了经济平稳健康发展和社会大局稳定,朝着实现全面建成小康社会的目标迈出了新的步伐。在极为错综复杂的国内外形势下,我国经济社会发展取得这样的成绩来之不易,需要倍加珍惜。这是以习近平同志为核心的党中央举旗定向、谋篇布局、坚强领导的结果,是习近平新时代中国特色社会主义思想全面引领、科学指导、成功实践的结果,是全党全国各族人民团结一心、砥砺前行、真抓实干的结果。
Overall, the main targets and tasks in economic and social development for 2018 were well accomplished. We got off to a good start in the critical battles against potential risk, poverty, and pollution, continued driving forward supply-side structural reform, and elevated the intensity of reform and opening-up. Living standards continued rising; economic development was kept on a stable, sound track; overall social stability was maintained, and we took fresh strides toward completing the building of a moderately prosperous society in all respects.
Given the extreme complexity of the domestic and international contexts, these achievements were not easily attained, and it is important to fully recognize their value. They are the result of the guiding principles and strategies, well-crafted plans and arrangements, and strong leadership provided by the Party Central Committee with Comrade Xi Jinping at its core; the result of the overall vision, sound guidance, and successful practices offered by Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era; and the result of the strong unity, firmness of purpose, and pragmatic and persistent efforts of the Party and the Chinese people of all ethnic groups.
从2018年经济社会发展情况看,经济增长、就业、价格总水平、国际收支平衡等主要指标保持在合理区间,创新驱动、资源节约、生态保护、社会保障等反映高质量发展的指标进一步改善,19个约束性指标中,18个指标完成全年目标,万元国内生产总值用水量下降指标完成情况与全年目标存在差距。该指标2018年计划目标为下降5.2%,初步统计数为下降5.1%,低于计划目标0.1个百分点。主要原因是,2018年全国降水量下降使得地表水资源总量减少约800亿立方米,部分地区受干旱影响,农业从河流抽取的灌溉用水量增加;南水北调工程向华北地区进行生态补水,全国生态用水量较2017年有较大增加,综合因素使得万元国内生产总值用水量降幅低于全年目标0.1个百分点。
From an economic and social development standpoint, the major indicators, such as economic growth, employment, the CPI, and the balance of payments, all remained within an appropriate range in 2018, while there were further improvements for indicators that reflect the quality of development, such as innovation capacity, resource conservation, environmental protection, and social security.
Of the 19 indicators with obligatory annual targets, 18 met their targets, while there was a discrepancy between the projected target for water consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP and the actual performance. The target for 2018 was a 5.2% decrease; however, according to preliminary statistics, the actual decrease was 5.1%, 0.1 percentage point lower than the targeted figure. The main reasons for this are as follows: Due to a drop in annual precipitation in 2018, China’s total surface water resources decreased by 80 billion cubic meters, and more water was drawn from rivers used for agricultural irrigation in some drought-affected regions. As water ecosystems in northern China were replenished with water from the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China’s water consumption for ecological purposes increased significantly compared with 2017. All these factors resulted in the above 0.1-percentage-point discrepancy.
46个预期性指标中,44个指标运行情况符合或好于年度预期目标,但社会融资规模存量增长率和城镇居民人均可支配收入指标实际运行值与预期值存在一定差距。关于社会融资规模存量增长率,该指标2018年预期目标为“与2017年实际增速基本持平”,2017年末社会融资规模存量增长13.4%,2018年末实际增长9.8%,与预期目标存在一定差距。为了给供给侧结构性改革营造适宜的货币金融环境,在对实体经济提供稳定融资支持的同时,主动采取了规范地方政府隐性债务以及合理控制投向房地产、环评不达标企业、产能过剩等领域的资金和抑制资金脱实向虚、减少资金空转等措施,社会融资规模存量增长率虽低于预期目标,但与名义GDP增长基本匹配。关于城镇居民人均可支配收入增速,该指标2018年预期目标为“与经济增长基本同步”,2018年GDP增长6.6%,城镇居民人均可支配收入实际增长5.6%,与预期目标存在一定差距。主要是受经济下行压力加大、实体经济特别是小微企业困难增多、部分行业企业利润有所下滑等影响,工资性收入等增长放缓,使得全国城镇居民人均可支配收入增速低于预期目标。
Out of the 46 indicators with anticipatory targets, 44 either met or surpassed targets. The actual growth of aggregate financing in the economy and per capita disposable income of urban residents fell somewhat short of the targets.
The growth of aggregate financing for 2018 was targeted to be roughly in line with the previous year’s actual growth rate. With growth in real terms of 13.4% at the end of 2017, the 9.8% figure at the end of 2018 was short of expectations. The reasons for this are as follows: To create a favorable monetary and financial environment for supply-side structural reform, we took measures to regulate the hidden debts of local governments and to appropriately control the flow of funds to the real estate sector, to enterprises that failed environmental impact assessments, and to industries with overcapacity. We also sought to prevent funds from being diverted out of the real economy and from circulating solely within the financial sector. At the same time, we continued ensuring stable financing support for the real economy. The growth of aggregate financing for the year fell short of the anticipatory target, but it was still basically in keeping with GDP growth in nominal terms.
Urban per capita disposable income in 2018 was targeted to stay largely in step with economic growth. GDP growth in 2018 was 6.6%, and urban per capita disposable income increased by 5.6% in real terms, lower than the anticipatory target. This can be attributed to the increasing downward pressure on the economy, more difficulties in the real economy, especially for small and micro enterprises, a decline in the profits of enterprises in some sectors, and slower growth of salary-based incomes.
同时,我们也清醒认识到,经济运行总体平稳、稳中有进,但稳中有变、变中有忧。从国际形势看,世界大变局加速深刻演变,全球动荡源和风险点增多,我国外部环境复杂严峻。世界经济虽有望延续复苏态势,但保护主义、单边主义加剧,主要发达经济体货币政策调整的外溢效应持续显现,部分新兴经济体面临的风险增多,国际大宗商品价格波动加剧,地缘政治风险累积发酵,全球经济贸易增速趋缓。从国内形势看,一是经济面临下行压力。内需增长放缓,基础设施、制造业、房地产开发等领域投资保持平稳增长的难度加大。受居民增收困难较多、汽车等传统消费放缓等因素影响,消费稳定增长面临挑战。二是农业农村基础仍然薄弱。农业科技水平仍待提升,农村基本公共服务供给和基础设施建设仍然滞后,农民增收渠道有待拓宽。三是实体经济面临困难增多。民营企业特别是小微企业融资难融资贵问题尚未有效解决,存在对民营企业惜贷压贷甚至直接抽贷断贷的现象,能源、原材料、人工、用地等成本较高,企业盈利空间受到挤压。营商环境有待进一步优化,公平竞争的市场机制尚不完善,产权和知识产权保护仍不充分,亲清新型政商关系仍不健全。四是高质量发展的短板制约仍待突破。重大原创性科技成果不多,一些关键核心技术受制于人,科技成果转化效率不高。产业结构还需进一步优化,发展新动能仍然不足。部分地区能源资源约束趋紧,生态环境问题依然突出。五是区域分化态势仍在持续。中西部一些地区结构调整难度较大,一些地区要素吸引力较弱,人才等优质要素资源外流比较严重,发展困难可能会增加。六是重点领域风险压力较大。外部环境不确定性可能通过贸易、跨境资本流动、大宗商品市场等渠道,加大我国输入性风险,国内股市、债市、汇市、互联网金融和房地产的风险隐患不容忽视。七是社会民生领域还存在不少问题挑战。部分省份就业结构性矛盾显现,居民持续增收制约因素增多,教育、医疗、养老等公共服务供给不足,人口老龄化程度不断加深。同时,我们在工作中还存在一些不足,有的政策制定的前瞻性、针对性、有效性还不够,没有充分考虑企业的适应程度问题;有的政策部门间统筹协调有待加强,有的改革举措和政策落实效果不彰,有的专项规划和项目建设需要及时启动;有的地方在政策执行过程中存在简单化、“一刀切”的问题。
Recognizing our achievements, we are also keenly aware that although the performance of the economy is stable and improving, this stability is punctuated by changes, some of which give cause for concern.
From an international standpoint, we are facing major changes that are deepening and evolving at a faster pace, and the sources of disruption and risk are increasing. These factors make for a complicated and grave external environment for China. Continued recovery of the global economy can be expected. But protectionism and unilateralism are intensifying, the spillover effects of monetary policy adjustments by major developed economies are becoming more evident, and some emerging economies are facing greater risks. The prices of major commodities are fluctuating sharply, geopolitical risks are building, and world economic and trade growth are slackening.
Domestically, there are also unfavorable factors. First, China’s economy still faces downward pressure. Slowing domestic demand growth is making it harder to sustain steady investment growth in the three major areas of infrastructure, manufacturing, and real estate development. We also face challenges in ensuring steady growth in consumer spending due to the many difficulties in increasing personal income, and softer growth in traditional forms of consumption like purchases of automobiles.
Second, the foundation of agriculture and rural infrastructure remain weak. The level of agricultural technologies needs to be improved, basic public services and infrastructure construction lag behind in rural areas, and broader channels need to be developed for rural residents to increase their incomes.
Third, the real economy faces mounting difficulties. Private companies are still finding it both tough and expensive to access financing, particularly small and micro companies. There is also some reluctance to lend to private companies and there are cases of loans being withheld, withdrawn, or cancelled. Enterprise profits are being squeezed by the rising costs of energy, raw materials, labor, and land use. The business environment requires further improvement. Flaws still exist in the market mechanisms for ensuring fair competition, more protection is needed for property and intellectual property rights, and there is still work to be done in building a new type of cordial and clean relationship between government and business.
Fourth, points of weakness affecting high-quality development need to be addressed. We produce a low number of major original scientific and technological outputs, rely too much on others for key and core technologies in certain fields, and perform poorly in putting scientific and technological achievements into practical application. Our industrial structure needs further improvement, and stronger growth drivers need to be fostered. In certain localities, energy and resource constraints are tightening and ecological and environmental problems are still grave.
Fifth, regional disparities continue to grow. Some localities in the central and western regions face grave difficulties in making structural adjustments, while other areas do not hold enough appeal to keep factors of production, leading to a serious outflow of talent and other high-quality factors. These issues have the potential to exacerbate the development problems of these areas.
Sixth, potential risks in key areas are grave. External uncertainties have the potential to intensify the inflow of risks into China through trade, cross-border capital flows, and commodity markets. Meanwhile, risks at home in the stock, bond, and foreign exchange markets, in internet finance, and in real estate cannot be overlooked.
Seventh, there are many problems and challenges affecting the people’s wellbeing. Structural employment problems have emerged in some provinces, and the factors hindering personal income growth are increasing. There is insufficient supply in education, healthcare, elderly, and other public services, and the problem of population aging is becoming more serious.
Shortcomings can also be identified in our own work. Some of our policies are not as forward-looking, targeted, or effective as they need to be, and they fail to fully take into account the adjustments they impose on enterprises. Coordination between some government departments needs to be strengthened to ensure effective implementation of reform measures and policies and to see that special plans and projects are launched promptly. And some localities tend to implement policies in an oversimplified or one-size-fits-all fashion.
对上述问题,我们将高度重视,既要增强忧患意识、坚持底线思维,抓住主要矛盾,有针对性地加以解决,有效防范各类风险连锁联动、叠加传导;又要紧扣社会主要矛盾的变化,全面用好我国发展的重要战略机遇期,保持战略定力、坚定必胜信心,化挑战为机遇、变压力为动力,加快推动经济高质量发展。
These are issues that we must take very seriously. In responding to them, we will raise our awareness of potential dangers, remain mindful of worst-case scenarios, focus on prominent problems, and take targeted measures that deliver solutions and effectively prevent risks from coalescing into chain reactions and causing ripple effects. We will respond to the change in the principal contradiction in Chinese society and take full advantage of the important period of strategic opportunity for China’s development. We will maintain strategic focus, firm up our confidence of success, and turn challenges into opportunities and pressure into motivation, in order to spur high-quality economic development.
余下部分扫描二维码查阅:


